HR Analytics and Employee Turnover: how to reduce the number of employees leaving the company
Employee turnover, particularly when undesired, presents a substantial challenge to organizations, leading to high costs, disrupted business continuity and potential customer dissatisfaction. Given the current tight labor market, managing employee turnover is a hot topic within HR, and it is particularly relevant to the insurance company. Anticipating a potential employee gap in the upcoming years, the organization aims to reduce the number of voluntary employee departures. To achieve this goal, they have enlisted the help of AnalitiQs.

What does employee turnover mean in the context of HR Analytics?
In the strictest sense, any employee leaving the company constitutes employee turnover. However, unwanted turnover refers to instances when a high-performing employee – who the organization would prefer to retain – decides to leave.
Employee turnover can be quantified annually using the following formula:
Number of leavers / ((number of employees at the beginning of the year + number of employees at the end of the year) / 2)
Analyzing employee turnover
To effectively reduce employee turnover, it is crucial first to understand annual employee turnover, underlying causes and the impact of these causes. Our organization was experiencing a 5 per cent annual voluntary turnover, with the majority of exits being attributed to better career opportunities, dissatisfaction with job roles, personal reasons, dissatisfaction with rewards and commuting distance.
AnalitiQs' role in tackling Employee Turnover
AnalitiQs performed a turnover analysis to clarify the key factors predicting voluntary turnover. This process consisted of three sequential steps: bivariate analysis, feature importance analysis and tree analysis.
Step 1: Bivariate Analysis
The first stage involved a bivariate analysis of the organization's HR system data. This statistical technique probes the correlation between various factors, such as age, time in grade and recent promotions, with voluntary turnover. Factors displaying a strong correlation with turnover were subsequently carried into the next stage of the analysis
Step 2: Feature Importance Analysis
The second step in the process was the feature importance analysis. Each factor's "importance" score reflects its potential impact on the model predicting turnover. Factors with higher scores were deemed to have a more significant influence on the model and were thus selected for the final analysis
Step 3: Tree Analysis
The third and final stage comprised a tree analysis, utilizing the highest-scoring variables from the previous step. The goal here was to identify specific risk factors and employee groups that exhibited a heightened risk of voluntary turnover
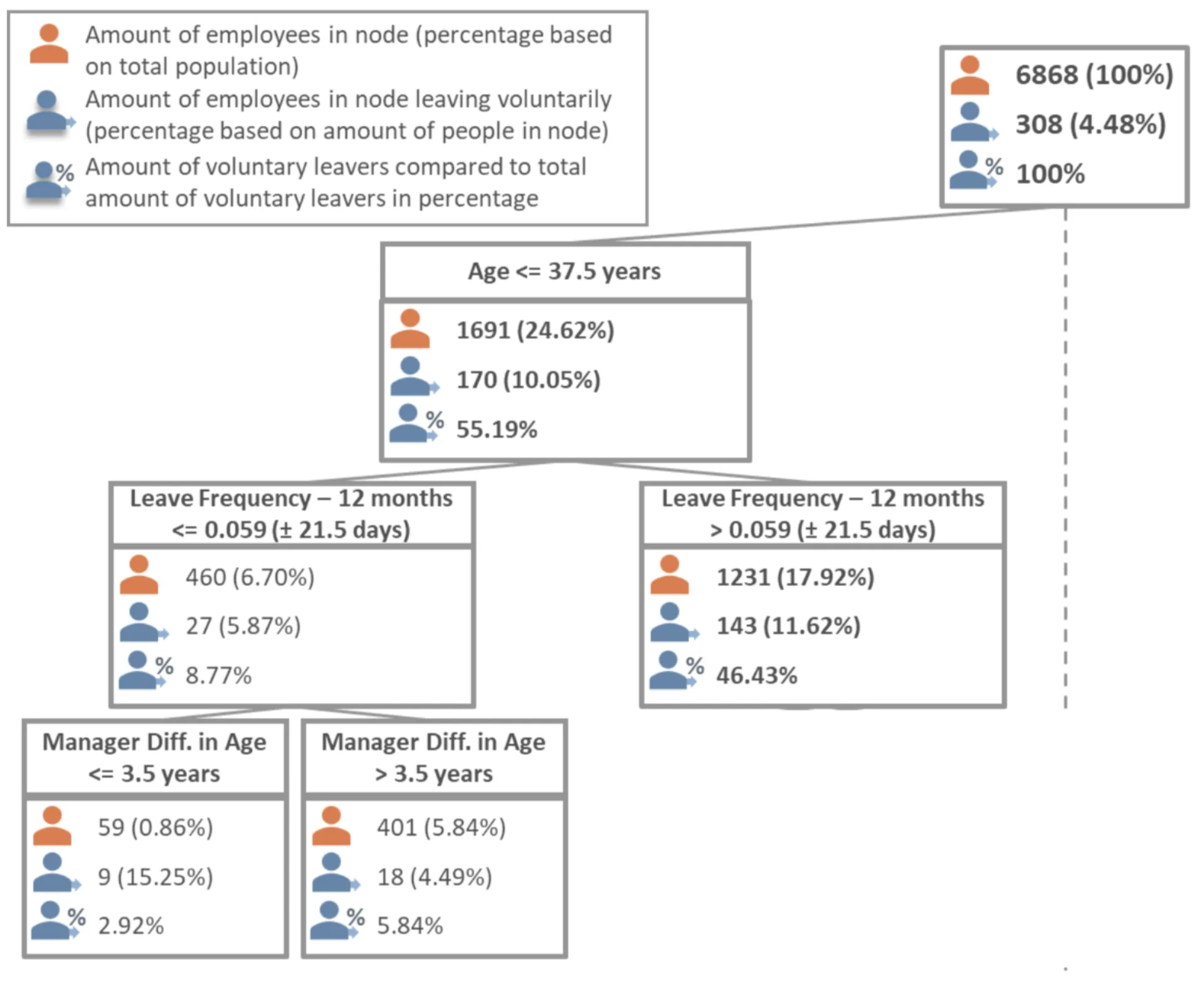
Valuable insights of the analysis
This comprehensive analysis delivered valuable insights for the organization. For instance, it was discovered that a particular group, composed of younger employees (under 40 years) with permanent contracts, was more likely to leave the company. This group, as it turns out, is considered the foundation and future of the company.
Furthermore, the tree analysis identified that within this young employee segment, those who had a higher number of leave days were more inclined to leave the organization voluntarily.
Conclusions and next steps
These findings have given the company direction and focus for further research into root causes. Questions to consider might be: Is there adequate support for employees juggling young families and demanding jobs? Is there enough flexibility to optimize work-life balance within this group of employees? By understanding these factors, the company can make targeted efforts to reduce voluntary employee turnover, ensuring its long-term stability and growth.
This case study attests to the power of data analysis in human resources management. It shows how an insightful, data-driven approach can lead to actionable solutions for addressing the challenges of employee retention.
Related Insights